IoT in healthcare: 10 examples of solutions & devices
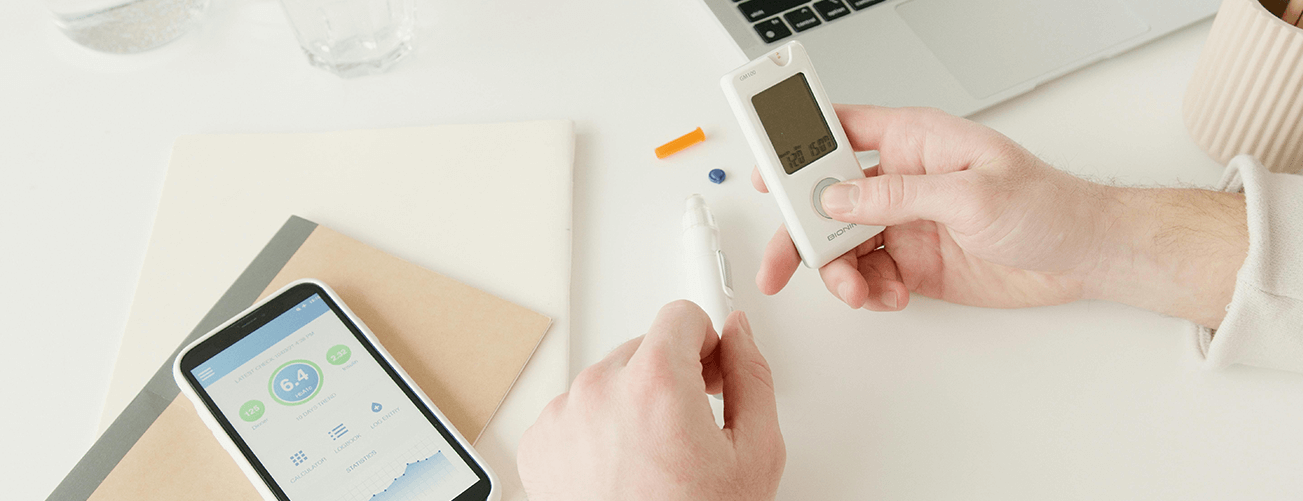

Telemedicine and the Internet of Things in healthcare started to show their real value during the pandemic. Many patients encountered difficulties in reaching their healthcare providers and opted for remote healthcare options instead. The Internet of Things for healthcare has rapidly expanded, with numerous use cases worldwide, ranging from better machine control to virtual medical assistance. This advanced technology has the potential to save lives by enabling rapid disease diagnosis and identifying suitable treatment options for patients.
How IoT is transforming the healthcare industry
IoT solutions in the healthcare sector are changing the game for all the participants: patients, doctors, and hospitals. So, how IoT is transforming the healthcare industry?
Healthcare Internet of Things provides new opportunities for remote patient monitoring, data collection, and analysis. IoT medical devices like wearables and sensors are used to automatically collect data on vital signs, heart rate, physical activity, and other health-related data.
The medical data can be transmitted to healthcare providers, who can then use it to monitor patient health and make informed decisions about treatment plans. Remote patient monitoring can help healthcare providers detect early signs of health issues and intervene before they become more serious.
IoT devices in healthcare can also help with medication management, reminding patients to take their meds on time and in the correct dosage. This leads to better treatment outcomes and reduces hospital readmissions.
Benefits of IoT in healthcare
IoT has the potential to improve pretty much any aspect of healthcare. Let’s mention just some of them.
Improved accessibility to healthcare
Remote patient monitoring and telemedicine allows patients to connect with healthcare specialists and receive the care they need without having to leave their homes. This is especially true for patients with disabilities.
Better decisions with more accurate data
IoT devices for healthcare provide continuous health monitoring resulting in more accurate data leading to better decision-making. Artificial intelligence assists in interpreting the results of medical tests, scans, and X-rays, pointing to potential issues.
Automation
IoT in healthcare is perfect at automating manual routines, be it data exchange, asset tracking, organizing workflows, climate control at home or in hospitals, notification, and more. Connectivity can take over tasks that previously required patients to travel to clinics or hospitals to see a doctor and get updates on the treatment plan.
Improved workflows
Digitization and cloud solutions are perfecting the way clinics manage their workflows and health data. Electronic health records replace tons of paper used to track medical history. Digital data is easier to manage, has less chance of being lost, and takes less physical space.
What can IoT do for healthcare?
Let’s review some general IoT applications in healthcare and how they can be used by various healthcare industry participants.
For patients
Various connected devices and wearables like fitness bands, glucometers, and heart rate meters help patients get insights into their health. This is especially important for patients who live alone or have chronic diseases. IoT healthcare applications help prevent health issues and facilitate their healthcare routines, making patients more autonomous.
For physicians
The use of medical IoT wearables and home monitoring IoT devices allows healthcare workers to track their patients’ health and get relevant and up-to-date data. The devices can send the data automatically, without bothering both patients and healthcare professionals by meeting each other in person.
For hospitals
IoT in hospitals and organizations can significantly improve the workflows. For instance, healthcare providers can improve their safety and security by using biometric scanners for access to sensitive areas. The Internet of Medical Things can be used to manage assets, monitor the environment, and track medical equipment like wheelchairs, defibrillators, oxygen pumps, and more. IoT in hospital can also help manage supply chains and avoid mistakes in their workflows.
IoT healthcare applications
Let’s consider some examples of IoT in healthcare: technologies, apps, and IoT solutions, and how the healthcare providers benefit from them.
1. Remote patient monitoring
Patients who aren’t physically present in healthcare facilities can have their heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and other personal health metrics automatically collected by IoT devices. This way, patients who get better in hospitals but need some observation, can be discharged sooner and get back to their usual lives faster staying under required supervision. Such a solution allows hospitals to use the resources optimally, leading to reduced costs without sacrificing high-quality care.

2. Big data
To enhance decision-making, the healthcare industry relies significantly on data, collected from IoT devices. Big data can help optimize care for individual patients and improve population health. One of the examples of big data in healthcare is EHR — an electronic clinical record that can include a continuous stream of data collected from IoT devices as well as data entered manually. With the collection of more precise and relevant real-time data, we can expect significant advancements in the medical field in the future.
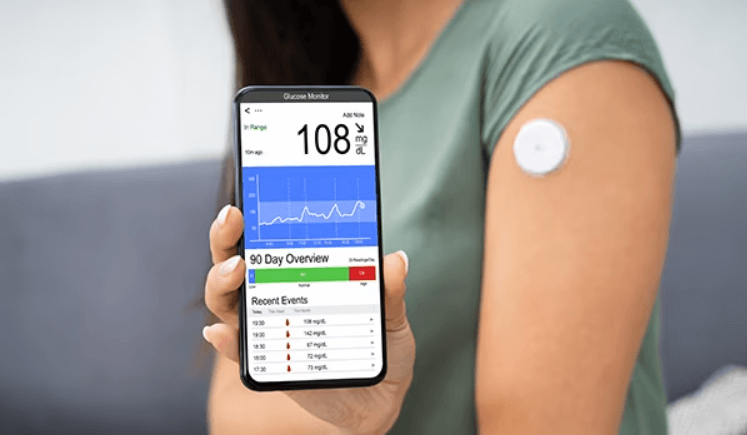
3. Glucose monitoring
For patients with diabetes, there are smart devices called continuous glucose monitors, or CGM. These are sensors placed under the skin that measure glucose levels in fluid between the cells. Such a sensor eliminates the need to prick the finger to check the glucose level. The device is usually paired with an app that can send reminders and show insights into the patient’s health. IoT in medical devices like CGM can also have a built-in pump that automatically delivers the required dose of insulin based on the results of the glucose level measurements.
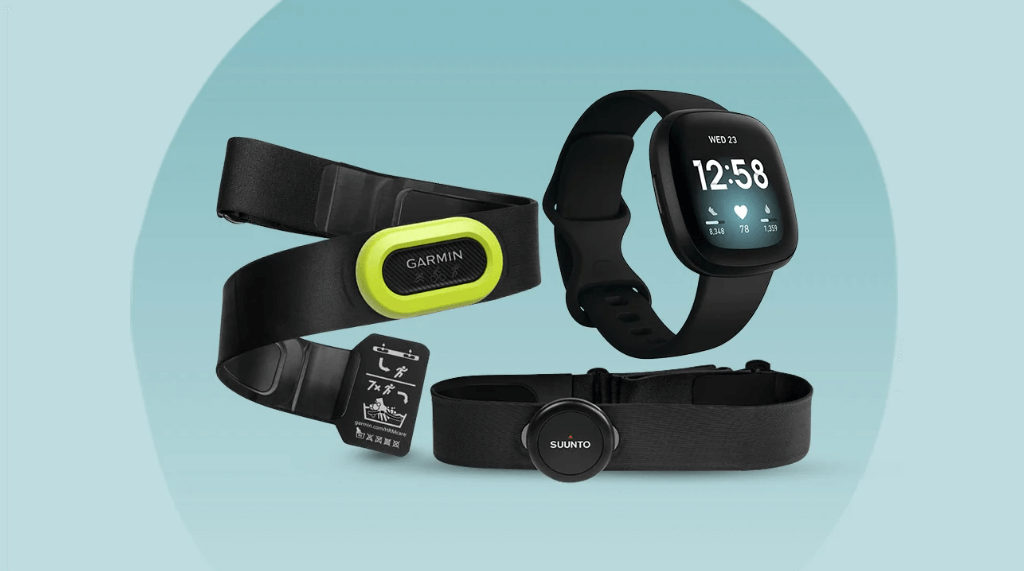
4. Heart rate monitoring
Monitoring heart rate is a somewhat challenging task as periodic examinations probably will miss a lot of sudden changes in heart rate, and constant monitoring requires the patient to be connected to the system all the time. Heart rate control is a necessary part of patient care during surgeries, recovery, or in critical care situations. Smart devices can record the heart rate so the healthcare team can see the patient’s data and check on any abnormalities that could have occurred. Heart rate monitoring is also useful for athletes, people struggling with anxiety, or individuals wanting to know how many calories they have burnt.

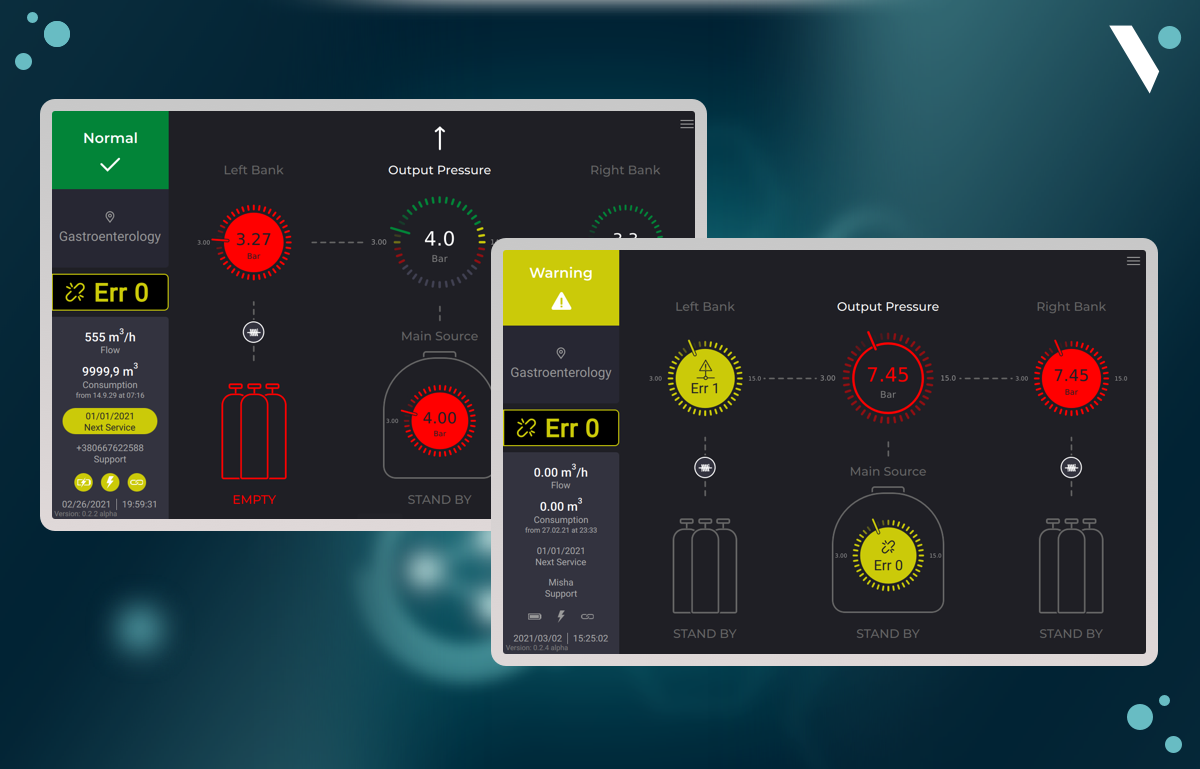
5. Medical systems management
Hospitals and clinics may have complex systems for delivering various medical gasses. Controlling the gas supply and ratio manually can be quite challenging and even risky, as the system should work stable. For cases like this, a good solution would be to rely on IoT for healthcare or an embedded system. That was exactly what one of our clients did. We created a solution for visualizing the usage of gasses and data changes and it worked as required.
6. Location services
This solution is good for tracking various medical equipment within the hospital, and beyond. Items like wheelchairs, defibrillators, pumps, and scales can be tagged with IoT sensors so that healthcare personnel can quickly find a spare item, or find the misplaced ones. In addition, location services can be useful for suppliers transporting small devices or healthcare products that can be easily stolen. IoT tags allow for tracking the items so it will prevent them from being lost.

IoT medical devices
7. Wearables
There are a great deal of wearable devices that can track various vital signs. They can be general-purpose like fitness trackers, smart watches, smart bands, or even smart clothes. These devices give general insights into the user’s activity and health. There are also wearables made for specific medical use, these are CGM, blood pressure trackers, heart rate trackers, and other health systems.

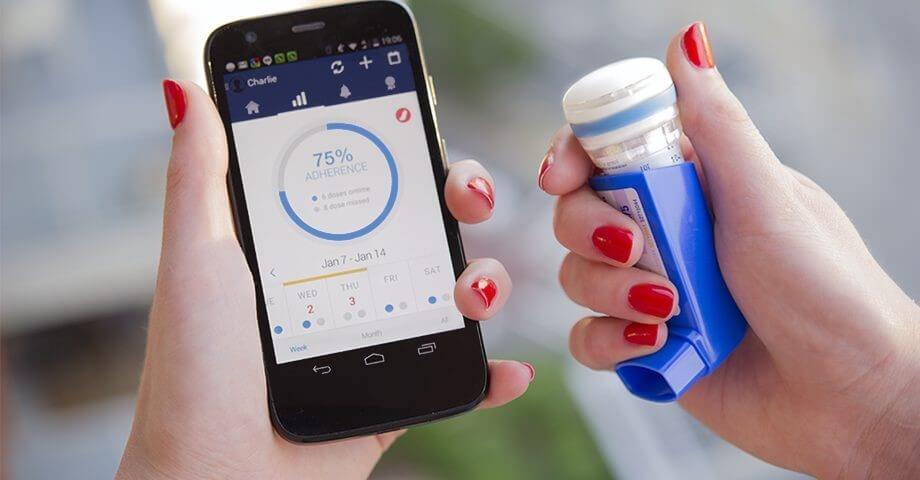
8. Connected inhalers
Inhalers are used by patients with asthma and other obstructive pulmonary diseases.
To alleviate the symptoms, patients must follow a strict medication schedule. However, often patients violate the treatment schedule or fail to stock refills beforehand. Here’s where smart inhalers may help. They connect to a mobile app via Bluetooth and use sensor technology to record usage time, date, and location. The app can send reminders for the next dose and alert users when they use the inhaler incorrectly or forget to take the device with them.

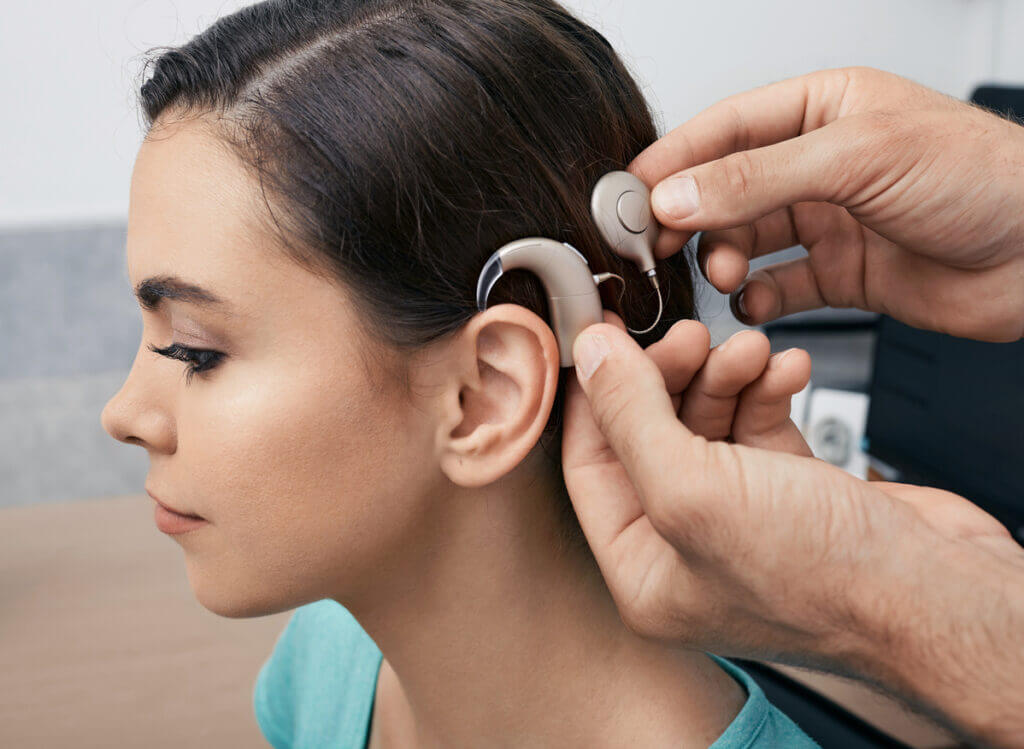
9. Smart implants
These devices are designed to be implanted into the human body to monitor, diagnose, or treat medical conditions. They include cardiac implants to treat arythmias; neurostimulators that address Parkinson’s disease and chronic pain; cochlear and retinal implants that help people with audial and visual disabilities; smart prosthetic devices that allow controlling the prosthetic more effectively. IoT for medical devices like implants is a crucial feature that broadens the functionality of the device, improves patient care, and allows for a better examination of diseases and symptoms.

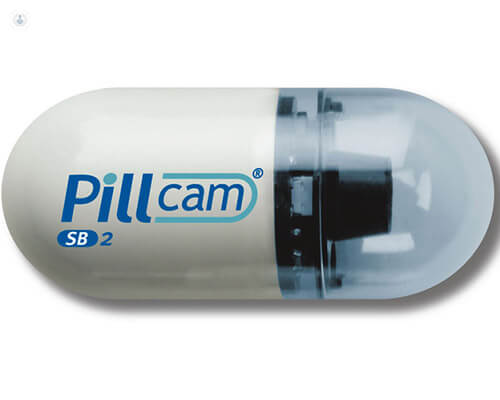
10. Ingestible sensors
The primary goal of such a sensor is to provide a less-invasive way to gather information from the digestive tract. These are devices that look like a pill or capsule that can be easily swallowed. When they are inside the body, they can measure pH levels, capture images, detect internal bleeding, or deliver drugs. Such a sensor would significantly help in diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases, making examinations like endoscopy way less painful for patients.

Importance of security for the Internet of Things in healthcare
Health information is extremely sensitive data that must be adequately secured and protected. That’s why various regulations like HIPAA exist: they regulate how the information is collected and used. If data storage and the Internet of things in healthcare are not properly secured, they can be hacked and the information stolen or misused.
Developing secure IoT hardware and software is the first step in addressing this challenge. The second step is to ensure proper usage and management of IoT devices to prevent sensitive patient data from being accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Another challenge is interoperability: to work effectively with the system and each other, the devices must be easily integrated and interconnected. This is not an easy task as a lot of IoT devices use proprietary protocols which makes it difficult to integrate seamlessly with the system.
These tasks are quite challenging, but not impossible. As healthcare providers are only starting their digital development, healthcare technology is evolving quite rapidly. AI and ML are currently on the verge of the entire IT world, so we’re to see a lot of impressive things in the foreseeable future.
Expanding the functionality and scope of IoT to enable smart healthcare
We already have multiple IoT healthcare use cases, but probably the best is yet to come. To fully unleash the Internet of Medical Things’ potential, it is important to expand the functionality and scope of IoT devices. This can be done by integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning technology into IoT devices.
Currently, IoT devices are perfect at automating routines and gathering data accurately, but we still aren’t ready to trust the device to interpret the data and rely on the diagnosis made by a machine. Here’s the time for AI and ML to come into play and make medical devices “smarter” and more autonomous in making decisions based on previous experience or learned data.
Conclusion
The potential of IoT in healthcare is rapidly gaining traction as a growing area of research. This technology provides a great opportunity for healthcare systems to proactively predict health issues, and diagnose, treat, and monitor patients both inside and outside the hospital. With the increasing adoption of technology-supported health services, healthcare systems can deliver flexible models of care that complement or replace traditional health service delivery practices through IoT. This will enable healthcare providers to expand their reach, improve patient outcomes, and provide a better quality of life for patients.




